The road marking industry plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, organisation, and efficiency of transportation infrastructure. From guiding vehicles to highlighting pedestrian zones and designating specialised parking spaces, road markings are an essential part of urban planning and road management. With the advent of new technologies and evolving transportation needs, such as micromobility and electric vehicle (EV) parking, road markings have become more varied and complex. This blog post will cover everything from road lines to pedestrian crossings, micromobility pathways, and specialised parking areas.
Road Lines: Rolls, Widths, and Colours
Road lines are perhaps the most recognised aspect of road markings. They guide vehicles, designate lanes, and improve safety by providing clear visual cues for drivers.
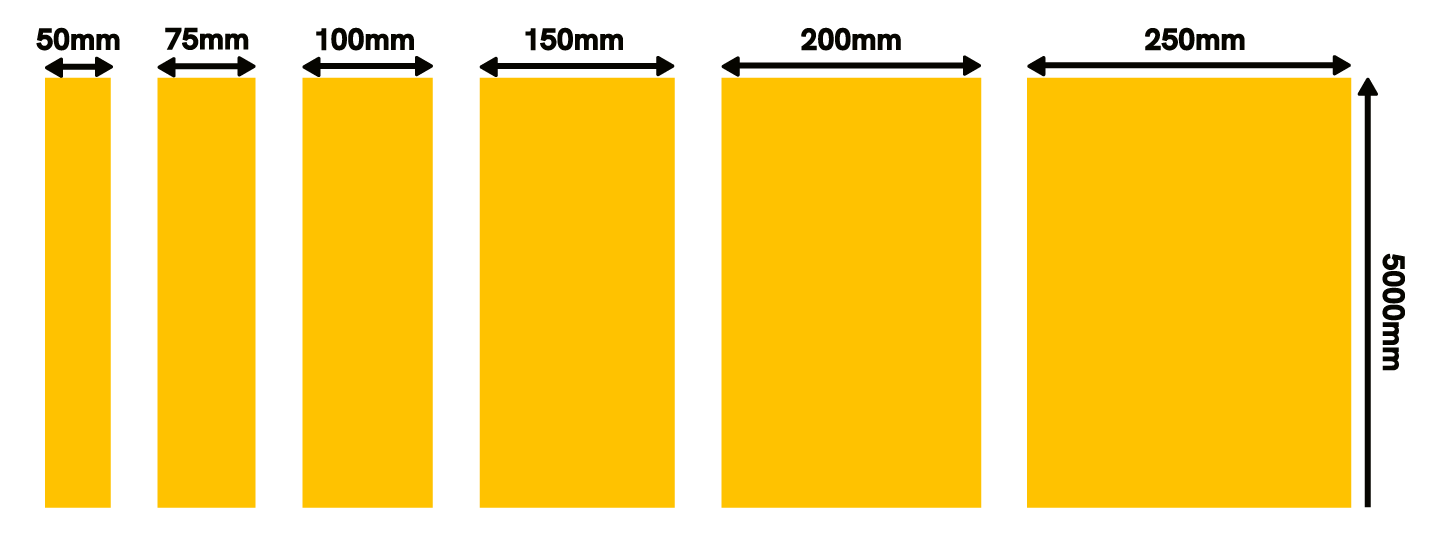
- Rolls and Widths: Road marking lines come in different widths, depending on their function and location. Wider lines are often used for highly trafficked areas to ensure better visibility and durability, while thinner lines might be suitable for less critical paths or low-traffic roads. Road line rolls, which are pre-formed thermoplastic rolls, offer a flexible and cost-effective solution for marking short stretches of road efficiently.
- Colours: The colour of road markings varies by country and function. White and yellow are the most common, with white often used to separate lanes of traffic moving in the same direction and yellow for regulation of parking and stopping. In some regions, blue is used for designated parking areas or for zones reserved for disabled parking, while red might indicate restricted lanes such as bus-only routes.

Directional Markings: Give Way, Stop, Keep Clear
Directional markings are crucial in controlling the flow of traffic and ensuring vehicles obey road rules. These markings are often larger and bolder to capture driver attention.
- Give Way: Triangular “Give Way” markings are often placed at intersections or junctions to indicate that drivers should yield to oncoming traffic. This marking is usually accompanied by a "Give Way" sign but also serves as a standalone reminder to slow down.
- Stop: “Stop” markings are typically located at intersections or railway crossings where vehicles must come to a complete stop. The word "STOP" is clearly marked in large white letters on the road, often coupled with a stop line to indicate where vehicles should halt.
- Keep Clear: These markings are used in areas where vehicles must not stop, such as in front of fire stations, hospital entrances, or near pedestrian crossings. "Keep Clear" markings ensure that vehicles don't obstruct access to critical zones.
Pedestrian Markings: Walkways and Crossings
Pedestrian safety is a top priority, especially in urban areas where foot traffic is heavy. Clear pedestrian markings are essential in managing the interactions between vehicles and people.
- Walkways: Pedestrian walkways are often marked by solid white lines that designate safe zones for walking in areas like shopping centres, warehouse floors, or factory facilities. These pathways help to keep pedestrians separated from vehicles or machinery.
- Crossings: Zebra crossings or other forms of pedestrian crossings are marked with broad white stripes that alert drivers to the presence of a pedestrian zone. These markings are commonly placed near schools, intersections, or public transport hubs where heavy foot traffic is expected.

Micromobility Markings: Bicycle Paths and E-Scooter Lanes
With the rise of sustainable transportation options, such as bicycles and e-scooters, cities are increasingly investing in dedicated micromobility lanes.
- Bicycle Paths: Bicycle paths are typically marked with solid lines and bike symbols to indicate their use. These lanes help cyclists navigate busy urban areas safely while reducing congestion on roadways shared with motor vehicles. Some cities have introduced colour-coded bicycle lanes (e.g., typically green or red) to make them more visible and to differentiate them from regular traffic lanes.
- E-Scooter Markings: As e-scooters gain popularity, specialised lanes and markings are becoming more common. These paths are designed to accommodate the unique speed and manoeuvrability of scooters, providing a safe and organised space for riders. Some urban are increasingly using shared lanes or dual-purpose micromobility lanes for both bicycles and e-scooters.

Parking Markings: EV, Disabled, Bicycle, and More
Parking markings have become more diverse as new transportation needs emerge, such as electric vehicle (EV) charging, micromobility parking, and zones for heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) and motorhomes. Clear markings are critical for maintaining the organization and safety of parking facilities.
- EV Charging Bays: Electric vehicle (EV) parking spaces are usually marked with distinct symbols and white parking bay lines (although sometimes other colours can be used, such as blue or green) to indicate that these spots are reserved for car charging. Markings are also used to indicate quick charging zones or areas where parking is limited to EVs only.
- Disabled Parking: Disabled parking spaces are typically marked with blue lines and the international symbol of access (a wheelchair icon). These spaces are often located close to building entrances for easier access and are wider than standard spaces to accommodate wheelchair access.
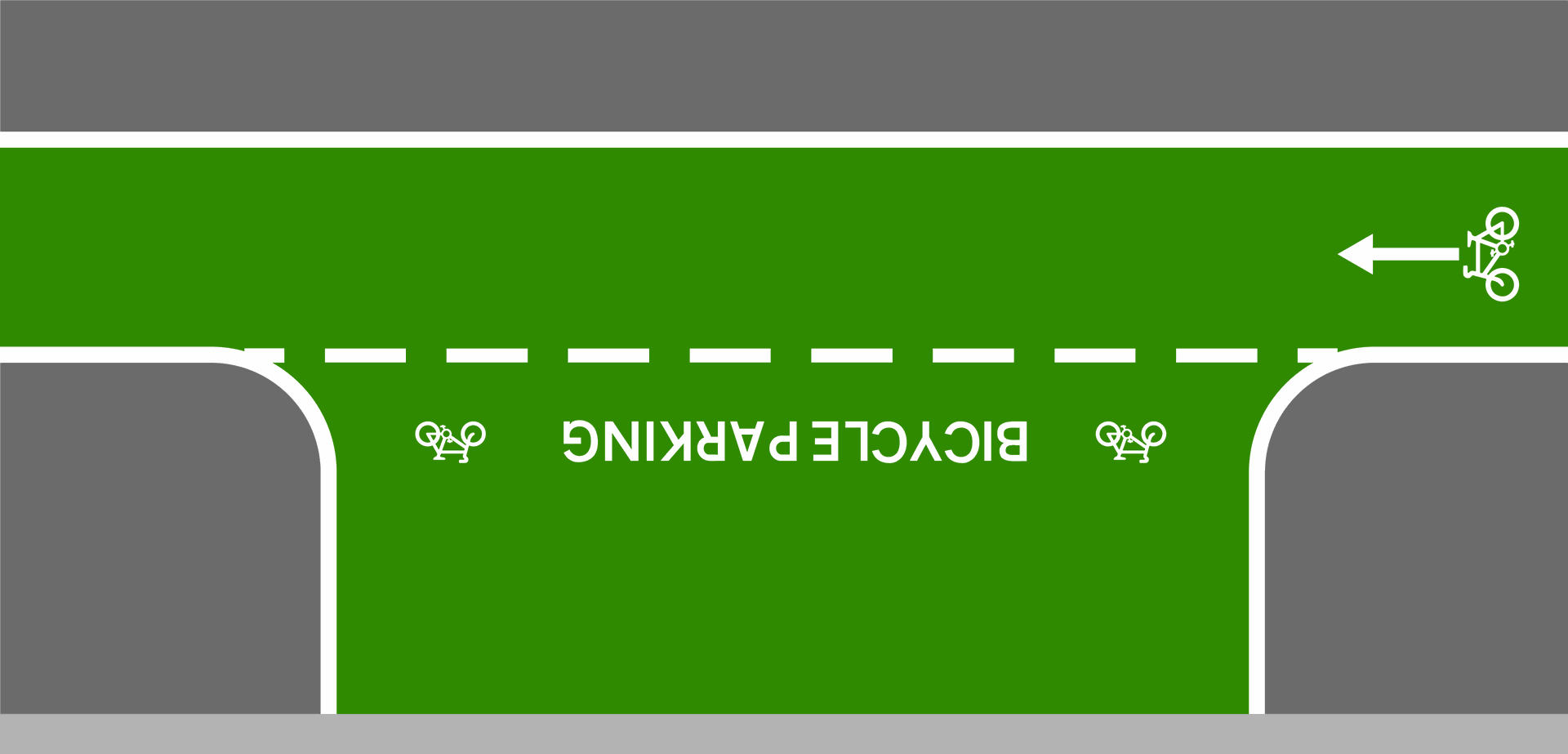
- Bicycle Areas/Sheds: Bicycle parking areas are marked with bike symbols and dedicated zones for locking bikes. In some urban areas, bicycle sheds or enclosed parking facilities offer safe, weather-protected spaces for cyclists to store their bikes.
- Motorcycle Parking: Dedicated motorcycle parking spots are often outlined with narrower lines than car parking spots and may include a motorcycle symbol for easy identification. These areas may also be equipped with secure mounting points for locking bikes.
- HGV/Motorhome Parking: Heavy goods vehicles (HGV) and motorhomes require larger, designated parking spaces due to their size. These parking areas are often marked in commercial zones, truck stops, or service stations along highways, with clear signage and markings to direct large vehicles.
- Quick Stay/Drop-off/Pick-up: Many public spaces, including airports, shopping centres, and schools, now have dedicated quick-stay or pick-up/drop-off zones. These areas are often marked with "Drop-Off" or "Pick-Up" symbols, and the time limit is clearly indicated on the road or curb.

Conclusion
As urban landscapes evolve and transportation needs diversify, road marking standards must adapt to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance. From basic road lines to specialised micromobility and parking markings, the road marking industry continues to develop new solutions that meet the demands of modern transportation systems. Whether it's designating bike lanes, highlighting pedestrian crossings, or managing EV charging spots, clear and effective road markings play a vital role in keeping people and vehicles moving safely and efficiently.