Directional road markings play a critical role in managing traffic flow, ensuring safety, and providing clear instructions to drivers. These markings guide drivers on when to stop, yield, or proceed, helping to avoid confusion at junctions and busy streets. Among the most common directional road markings are "Give Way," "Stop," "Keep Clear," and directional arrows, all of which contribute to safer roads and improved traffic efficiency.
In this blog post, we'll dive into the purpose and application of these essential markings, helping you understand how each functions and why they're critical for road safety.
Give Way Markings: Managing Traffic Flow at Intersections
Purpose: The "Give Way" marking is typically found at intersections and junctions, signalling to drivers that they must yield to traffic on the intersecting road. This marking ensures smooth traffic flow by reducing potential conflicts between vehicles approaching from different directions.
Visual Design: "Give Way" markings usually consist of a series of large triangular shapes pointing towards approaching drivers. These triangles are often accompanied by a "Give Way" sign to reinforce the instruction visually.
Where It's Used:
- At T-junctions where traffic from one road must yield to another.
- In roundabouts where vehicles entering must give way to those already circulating.
- On minor roads merging with major roads to prevent accidents.
Why It Matters: Without clear "Give Way" markings, drivers might enter intersections without proper caution, increasing the risk of collisions. These markings prevent confusion and help maintain safe and orderly traffic flow.
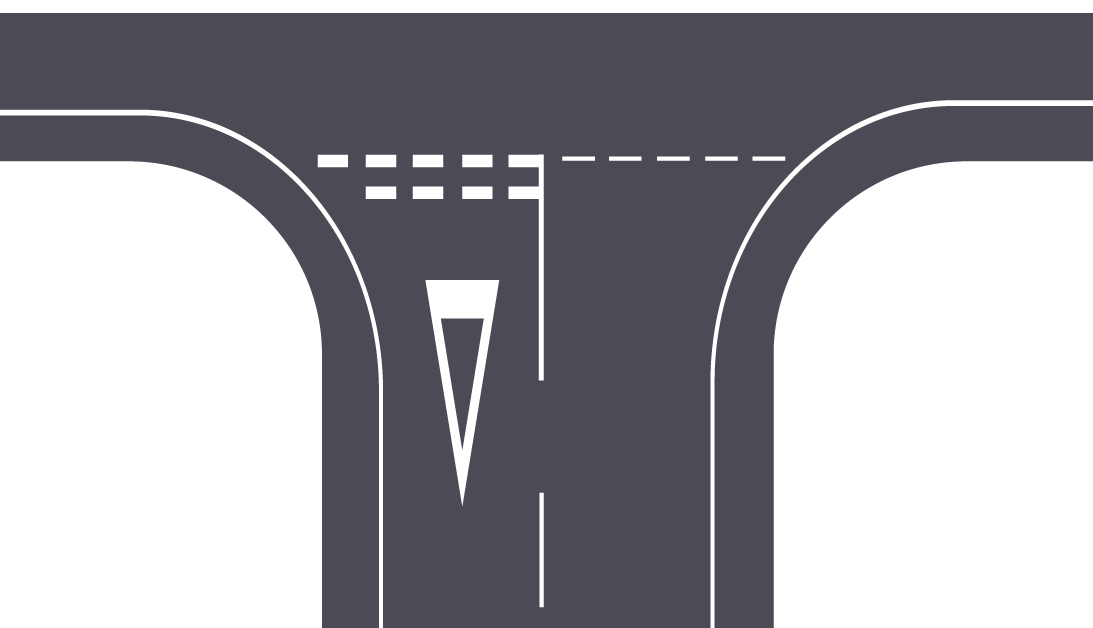
Stop Markings: Reinforcing Complete Stops for Safety
Purpose: "Stop" markings are placed at intersections where vehicles must come to a full stop before proceeding. This is especially critical at busy junctions, pedestrian crossings, or areas with poor visibility, where a failure to stop can lead to accidents.
Visual Design: The "Stop" marking consists of a wide, solid white line across the driver's path, usually paired with the word "STOP" painted in large letters just before the line. A corresponding "Stop" sign is often positioned nearby to reinforce the requirement.
Where It's Used:
- At major intersections where cross traffic does not stop.
- Near schools, pedestrian-heavy areas, or dangerous crossroads.
- At locations with obstructed views that require cautious vehicle entry.
Why It Matters: "Stop" markings compel drivers to make a complete halt, giving them the opportunity to observe surrounding traffic and proceed only when it's safe. This reduces the likelihood of collisions in high-risk areas.
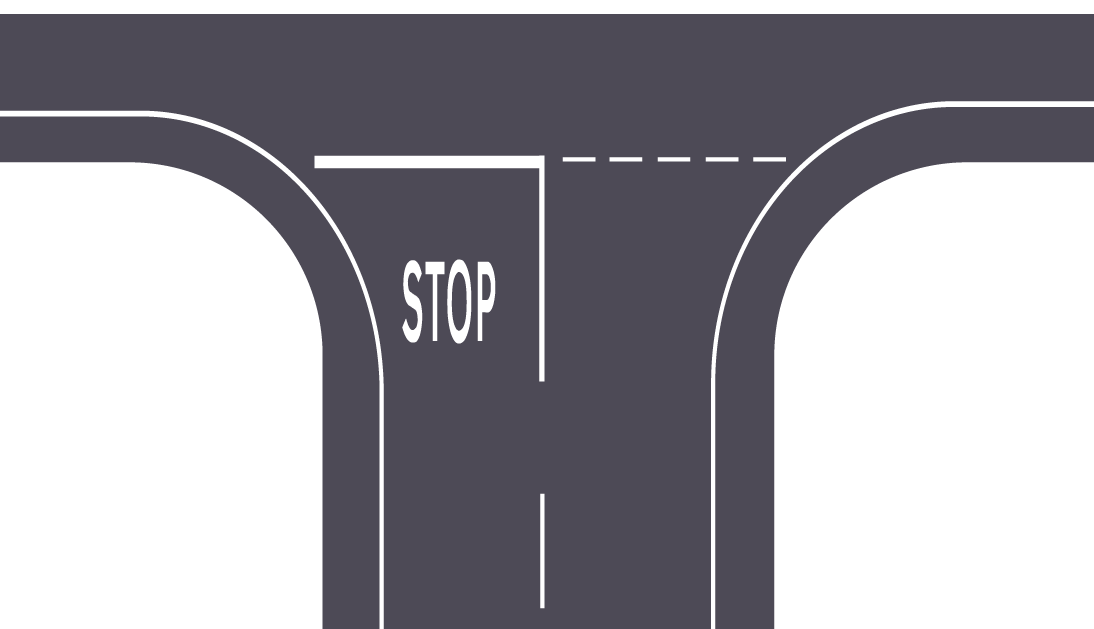
Keep Clear Markings: Preventing Blockages in Critical Zones
Purpose: "Keep Clear" markings are used to ensure that certain areas remain unobstructed by vehicles, especially in places where traffic congestion could lead to bottlenecks or blocked access. These markings are essential for maintaining access to driveways, emergency exits, and intersections.
Visual Design: The "Keep Clear" marking typically consists of the words "KEEP CLEAR" painted in large, bold letters on the road. These markings are usually surrounded by a hatched lines in a box or grid pattern to make them more noticeable.
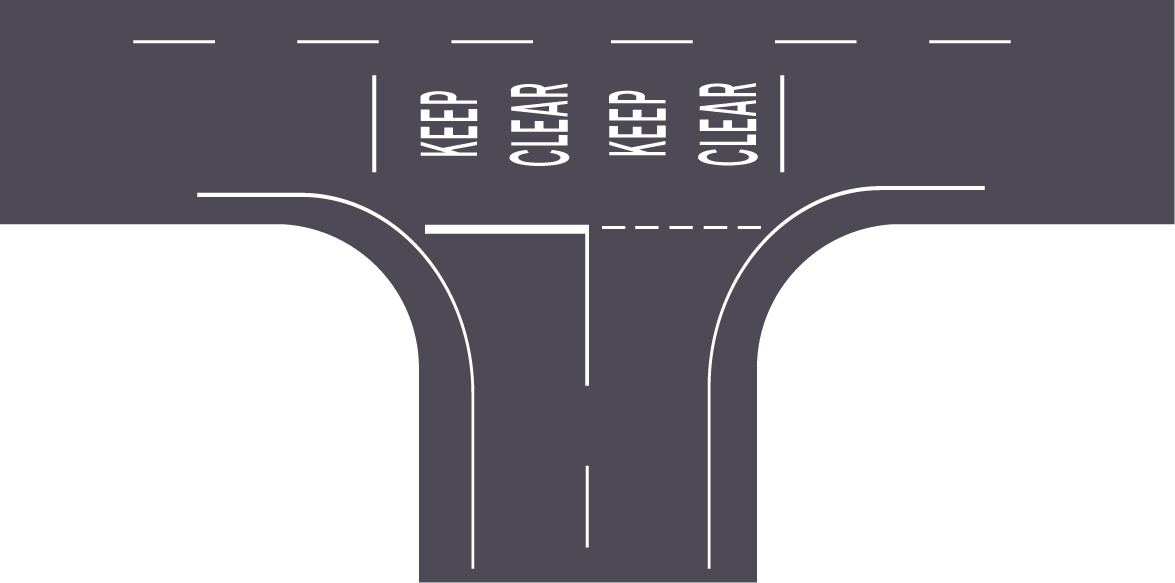
Where It's Used:
- At the entrances and exits of fire stations, hospitals, or other emergency facilities.
- Driveways to private properties, preventing blockage by parked vehicles.
- Intersections that are prone to congestion, ensuring smooth traffic flow even in heavy traffic.
Why It Matters: Without "Keep Clear" markings, vehicles could block key areas, hindering access for emergency services or causing unnecessary delays in traffic flow. These markings help prevent gridlock and keep essential zones free from obstruction.

Directional Arrows: Guiding the Way
Purpose: Directional arrows are perhaps the most versatile road marking, providing clear instructions to drivers about which direction to take. These arrows ensure drivers follow the correct paths, preventing confusion, accidents, or wrong-way driving on one-way streets.
Visual Design: Directional arrows can vary depending on the intended instruction. Common examples include straight arrows (indicating that drivers should proceed forward), curved arrows (indicating turns), and split arrows (indicating that drivers can choose between two directions, like left or right).
Where It's Used:
- At intersections to guide vehicles into the correct lanes for turning or going straight.
- On one-way streets, reinforcing the direction of traffic.
- In parking lots and multi-lane roads, ensuring drivers move into appropriate lanes well in advance of turns or exits.
Why It Matters: Arrows play a vital role in reducing driver uncertainty, especially in complex intersections or multilane roads. By guiding traffic with clear directional cues, these markings improve safety and reduce the risk of last-minute lane changes or wrong-way driving.
Conclusion
Each of these directional road markings—Give Way, Stop, Keep Clear, and arrows—serves a unique purpose in maintaining safe and efficient roadways. From ensuring that drivers yield appropriately at intersections to keeping critical areas clear of obstructions, these markings are an essential part of modern traffic management systems.
Understanding their importance and adhering to the rules they represent is key to preventing accidents, improving traffic flow, and making roads safer for everyone.